Revo-i: The competitive Korean surgical robot
Article information
Abstract
We aim to discuss the development of Revo-i, the first new robotic medical device for laparoscopic surgery made in Korea, including the history of launching Revo-i in the global market, and the success results of the progression with the clinical data after launching the system. Revo-i has been commercialized in the global and domestic market, and it has been increasing the number of the procedures at the major specialties such as obstetrics and gynecology, urology and general surgery. This shows that Revo-i is one of the competitive robots in the global market to compete with the current worldwide robotic system.
INTRODUCTION
Laparoscopic surgical robot market has been increasing since the very first laparoscopic surgical robot outcome in the global market. Recently, Meerecompany Inc. in Korea manufactured and launched a surgical robotic system named Revo-i. This is the first innovative laparoscopic surgical robot in Korea, which other major Korean medical companies could not develop robots for laparoscopic surgery ever before. Various companies have attempted to develop a competitive product, yet have failed to present their robotic systems to the market globally or even domestically due to the technical issues, cost-risk factors, and internal decision-making by their policy.
In this article, we aim to discuss the development of Revo-i, the first new robotic medical device for laparoscopic surgery made in Korea, including the history of launching Revo- i in the global market, and the success results of the progression with the clinical data after launching the system. At the end of the session, we would like to discuss the next generation of Revo-i surgical robotic systems, how it can be applied to diverse applications clinically, and the main-goal of the business by spreading out Revo-i surgical robotic systems to the marketplace for more patients through the positive benefits.
MARKET SITUATION IN SURGICAL ROBOT
Global surgical robot market
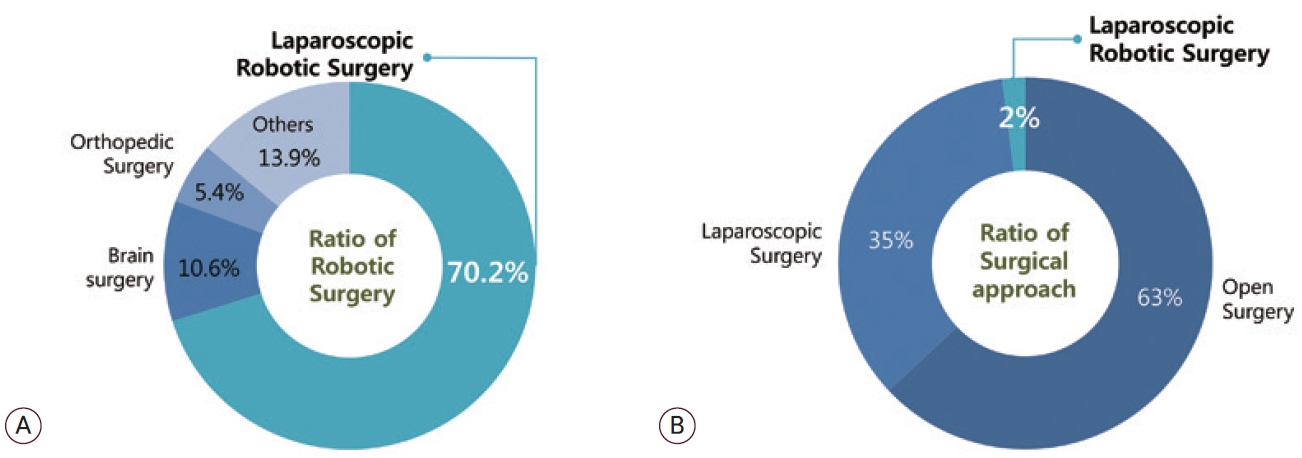
This section seeks to update the data regarding the global market size for surgical robots in laparoscopic, orthopedic, neurologic surgery [1,2]. The size of the global surgical robot market is expected to increase by 13.2% annually from 4 trillion 5,824 billion Korean won in 2015 to 9 trillion 6,413 billion Korean won in 2021. The main application area of surgical robots is laparoscopic surgical robots, accounting for 70.1% of all surgical robots, followed by brain surgery 10.6% and joint surgery 5.4%.
The global surgical robot market in laparoscopic surgery grows very rapidly, but the number of laparoscopic robotic surgeries is only 2% of all surgical operations including open surgery, laparoscopic surgery and robotic surgery (Fig. 1).
This ratio is gradually increasing, and considering only the 35% general laparoscopic surgery market, which is expected to switch to robotic surgery among the remaining 98% markets as the laparoscopic surgical robot market is expected.
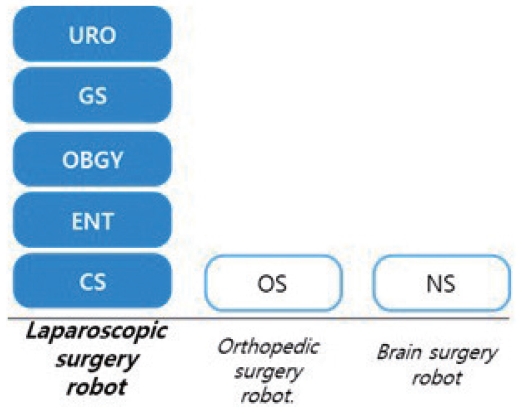
The applicable specialties for the laparoscopic surgical robot are in urology, general surgery; including hepatic pancreatic, gastrointestinal, and colorectal, obstetrics and gynecology, otorhinolaryngology, and thoracic surgery, and the scope of the application is very wide (Fig. 2) [2]. Orthopedic or neurosurgery surgical robots can only be applied to single or a few surgeries in their category.
Worldwide robotic surgery and installed base of global surgical robot
This section seeks to update the data regarding the use of surgical robots in laparoscopic surgery and the numbers of installed bases of surgical robots globally [3]. The number of procedures of laparoscopic surgical robots in the world is growing to around 18% every year. Specifically, the adoption of surgical robots is rapidly used in general surgery, gynecologic surgery, urologic surgery, cardiothoracic surgery, and head and neck surgery. Most of the procedures are performed in the United States because the first surgical robot system was installed in the United States and has been in operation since the 2000s. On the other hand, the major procedures volume is driven by urology in the rest of the world including Europe, Asia and the other continents. Still, we project that the size of the market for laparoscopic surgery can be penetrated by the surgical robot at the various surgical areas and the adoption rate for the laparoscopic surgical robot is also globally expected to increase over time (Fig. 3) [4].

Number of procedures in laparoscopic surgical robot (A) and number of installed base in laparoscopic surgical robot (B). Reused with permission from Meerecompany, Korea.
The number of installations in laparoscopic surgical robots shows an increase of 12% to 13% every year, except for 2020 due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. As of 2020, there are 5,989 surgical robots installed around the world, and by continent, the United States is the largest market that accounts for about 62% of the total market.
In terms of growth rate, the Asian market has the fastest growth (+15% year-on-year). The main reason for the rapid growth is because of the Japanese market, which is expanding its insurance coverage for some robotic surgery indications such as in urologic, colorectal surgery (Fig. 4).
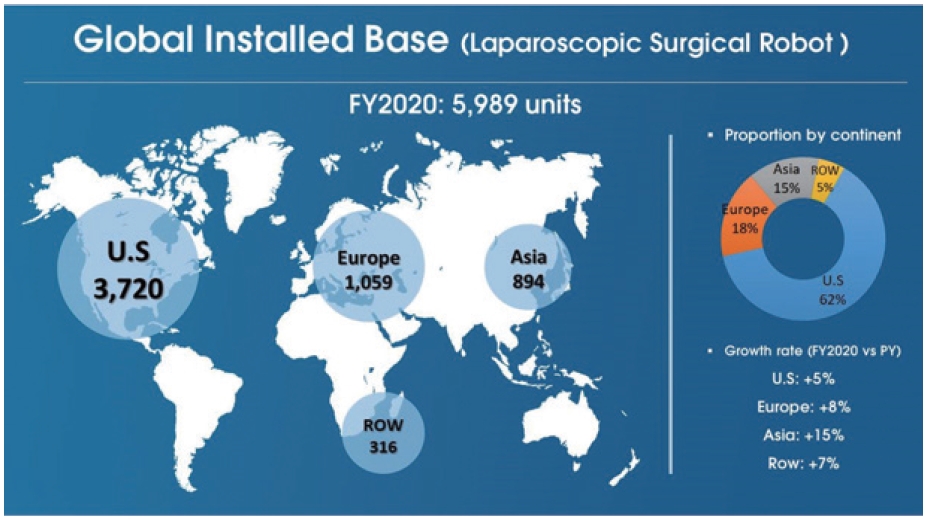
Global Installed base of laparoscopic surgical robot. Reused with permission from Meerecompany, Korea.
Demand for surgical robots may also be impacted because of the pandemic; however, there is still a need for robotic surgery in hospitals. Main reasons for these effects are due to advantages for surgical robots compared to laparoscopic devices (mostly instruments only) that may cause more surgeons fatigue during the surgery. We also experience hospitals' desire for surgical robots, and based on those needs, we continue to have interest and purchase requests for Revo-i. Of course, it is true that there are various risk factors such as economic conditions, budget cuts in hospitals due to COVID-19 pandemic, however, we will discuss how Revo-i can relieve the financial burden purchasing surgical robot later in the upcoming chapter of ‘Revo-i Surgical Robotic System’.
REVO-I SURGICAL ROBOTIC SYSTEM
Development and commercialization of surgical robots
Korea has a very high level of medical robot development in the world, shown by the second highest number of patent applications after the United States in 2017. Meerecompany is a corporation with world-class research capabilities in the fields of medical robot development, develops and manufactures Revo-i, laparoscopic surgical robot, and expands it into domestic and overseas markets (Tables 1, 2).
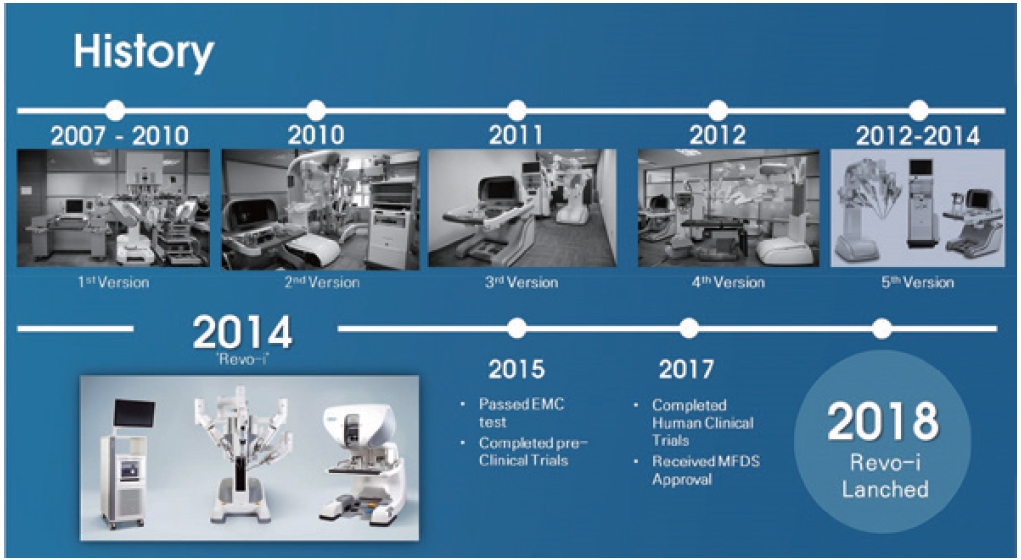
Meerecomany started the laparoscopic surgical robot business in 2007 and developed Revo-i with five prototypes. After multiple models and 20 different animal studies, they developed the current model in 2017. The latest model passed the pre-clinic test, EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) test, etc., to prove that it is secure to perform the surgery based on the standard regulation for medical devices. Furthermore, Revo-i completed the human clinical trial, and received approval of Ministry of Food & Drug Safety in August 2017. Revo-i was commercialized in 2018 and there are published data with case studies from human patients (Fig. 5).
Revo-i surgical robot systems
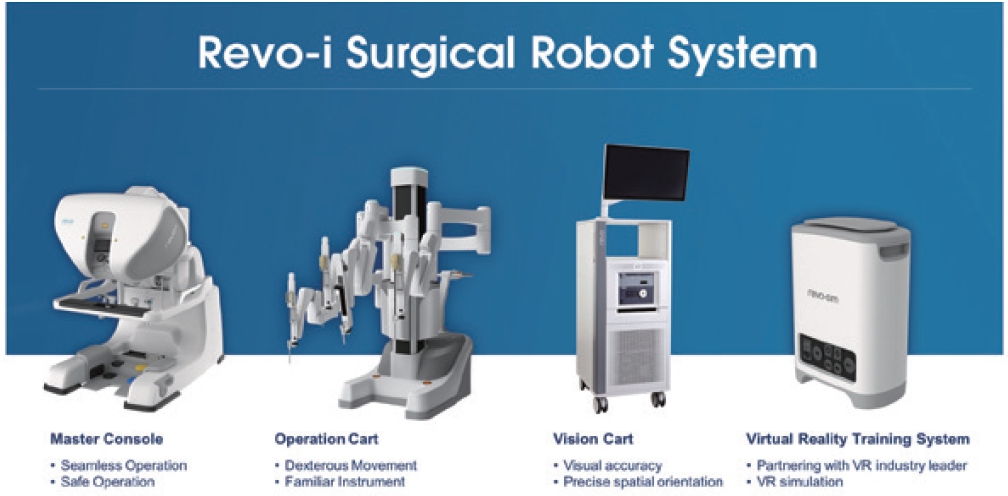
Revo-i is the world's second and the very first laparoscopic surgical robot in Korea. This system consists of three equipment: master console, operation cart, and vision cart (Fig. 6).
Surgeons perform robotic surgery at the master console to control the robotic arms of the operation cart. The master console's 3D HD viewer shows the surgical site with three dimensions. The master console has ergonomic settings where surgeons can comfortably adjust their seating height, 3D viewer slope, armrest height, etc. It may cause clinical advantages by reducing surgeon fatigue. Surgeons could control instruments and the endoscopic camera for the safety of robotic surgery. While surgeons control instruments, the motion of the surgeon’s hand is replicating the robotic arms. When it comes to manipulating camera control, it allows surgeons to easily move, change, zoom in/out, and rotate their surgical area of vision. Surgeons can reposition the controller to the comfortable position by finger clutch buttons and foot pedals [5].
Operation cart can be moved into the sterilization area, and it performs the surgery by using Instruments mounted on the instrument arm and the endoscope mounted on the camera arm. There are four arms, including one camera arm and three instrument arms. It operates like a surgeon's eyes and hands without tremors. The tip of the instruments and the direction of robotic arms can be moved by the surgeon's control.
The instruments of Revo-i are mounted on the operation cart and have a joint-shaped structure with 7 degrees of freedom, so it can move similarly to a human wrist, which is very helpful in managing the surgical area during the surgery [6]. There are 13 types including monopolar and bipolar energy instruments, forceps, needle holders, clip appliers. Also, it has a standard and long type that can be used if it needs to reach deeper areas (Fig. 7).
Vision cart has the imaging processing systems where it transfers the images taken by the endoscope not only to the master console with 3D images, but also to the monitor at the vision cart. In consideration of the staff in the operating room, a large 27-inch high-definition touch screen monitor is provided at the vision cart, and the multi-joint monitor arm helps staff easily position the monitor in the desired direction, so that staff can understand the actual surgery status. It also has the light-source and camera control unit to manage the surgical area for the right vision and safety. Recently, the specification of the Revo-i endoscope has been upgraded to deliver clear and precise 3D HD vision.
Revo-sim, a simulator that can be used with the master console, has also been developed to allow the surgeon to improve their surgical skills before using Revo-i. Revo-sim has three steps to learn how to use Revo-i. There are basic skills, suturing & anastomosis, and advanced procedures. These three steps will enhance the surgeon’s robotic skills so that the surgeons can use Revo-i more comfortably.
Safety and clinical effectiveness of Revo-i
In May 2021, Revo-i was designated as the first "Innovative Medical Device" by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety in the "advanced medical robot technology group" to prove stability and effectiveness.
Revo-i had conducted clinical studies such as prostatectomy, pylous-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy, and colon resection at Severance Hospital for expanding surgical indication, proving the value of the surgical robot [6-8].
At the same time, after Revo-i has been released in the medical devices market, Revo-i were installed in hospitals specialized in general surgery and gynecological surgery, and more than 200 surgeries have been performed with Revo-i (Table 3).
Benefits of Revo-i
As a laparoscopic surgical robot, Revo-i has various advantages compared to conventional surgery including laparoscopic surgery and open surgery. The positive surgical results of robotic surgery have already been proven through numerous clinical papers, such as accurate incision of the tumor site, low bleeding, and fast recovery of patients. Revo-i also contains those clinical benefits and surgeon’s benefits, which we discussed at the previous chapters describing Revo-i surgical system, by conducting surgeries to the patients at the hospital. But the biggest reason why it is difficult to popularize robotic surgery is the high cost.
And the second strength is open research and development. Even after its launch in 2018, it has continuously improved its performance and developed new instruments. The system optimization research has continued to reflect the user's opinion and the image quality and delay time of the surgical image were improved by changing the 3D endoscopic camera system. This has been giving more satisfaction to the potential users who are interested in Revo-i.
The last is a customized training program. All robotic surgery teams have to complete the training program provided by Meerecompany. It is a differentiated program that considers variables such as the type of hospital, medical department, and surgical approach based on an understanding of the operating room environment and the role of each team.
CONCLUSION
Revo-i has been commercialized in the global and domestic market, and it has been increasing the number of the procedures at the major specialties such as obstetrics and gynecology, urology and general surgery. This shows that Revo-i is one of the competitive robots in the global market to compete with the current worldwide robotic system.
Meerecompany has been actively performing sales and marketing activities to introduce and distribute surgical robots in university hospitals as well as general hospitals and private clinics. Also, they plan to increase reliability by accumulating clinical data for cancer diseases. One of their strengths is working with many medical staff to improve the quality of the Revo-i surgical system. Compared to the early stages of Revo-i, as a result, the system has become more stable and coupling capability between movement of the surgeon in the master console and robotic instrument has improved noticeably.
The vision of "Better care of more patients” of Meerecompany contains the direction of their pursuit. First, 'Better care' means that continuous research and development of surgical robots can bring better clinical care to patients. Second, achieving technical cooperation with competent companies also enhances the high-technology technique to make better robotic systems for surgeons' benefits. Lastly, they pursue quick-feedback to Revo-i users and reflect their opinion to Revo-i, surgical system. Therefore, Revo-i brings more benefits not only to surgeons but also to patients who need robotic surgery by distributing to university hospitals, general & specialized hospitals and private clinics globally. We expect Revo-i is becoming more spreading out to the market in order to commit to their mission, ‘better care for more patients’.